Can a simple scan truly unlock the secrets hidden within the intricate landscape of the human brain? Indeed, a Computed Tomography (CT) scan of the brain is a powerful diagnostic tool that can reveal a wealth of information, from the mundane to the life-threatening, offering a crucial window into the health of our most vital organ.
The landscape of medical imaging has witnessed remarkable advancements, and at the forefront of these innovations stands the CT scan, a technology that offers detailed insights into the brain's structure. This non-invasive technique utilizes X-rays to generate cross-sectional images, providing a comprehensive view of the brain, skull, and surrounding tissues. These images, in turn, can assist in the diagnosis of a wide range of conditions, from acute injuries to chronic diseases. A CT scan provides a detailed report encompassing both normal and abnormal findings, playing a crucial role in modern diagnostic imaging and patient care. The information is often so valuable, CT scans have become a cornerstone of diagnostic imaging, especially when time is critical in the identification and treatment of brain-related conditions. The results can sometimes provide a definitive diagnosis and at other times will point toward the possibility of abnormal conditions.
Let's delve into the intricacies of this invaluable diagnostic tool. A CT scan of the head utilizes a series of X-ray beams that pass through the brain from multiple angles. These beams are detected by sensors, and the data collected is processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images. These images, in turn, help medical professionals examine the brain's structures, identify abnormalities, and distinguish between different types of medical issues.
- Breaking Latest News On Lsu Qb Colin Hurley Updates Details
- Unlocking Hip Stability Ligaments Pain Recovery Your Guide
The versatility of brain CT scans is a significant advantage. They are particularly valuable in the assessment of acute conditions, such as head injuries, strokes, and bleeding within the brain. Moreover, CT scans can detect tumors, infections, and vascular disorders, playing a crucial role in timely and accurate treatment.
While CT scans provide a comprehensive view of the brain's anatomy, they also help reveal certain functional aspects. For example, the use of contrast agents can improve the detection of tumors and vascular anomalies. The contrast agent is often gadolinium, which enhances the visibility of tissues and structures within the brain.
The process of obtaining a CT scan is generally straightforward and non-invasive. During the scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a circular scanner. The X-ray tube rotates around the patient's head, emitting a series of beams. The whole process is typically quick, taking just a few minutes to complete. However, it's important to remain still during the scan to prevent motion artifacts that can affect the image quality.
- Best Mexican Haircuts Hairstyles For Men Trendy Looks
- Denise Clark Bradford Son Gino Morrison Iis Passing News Updates
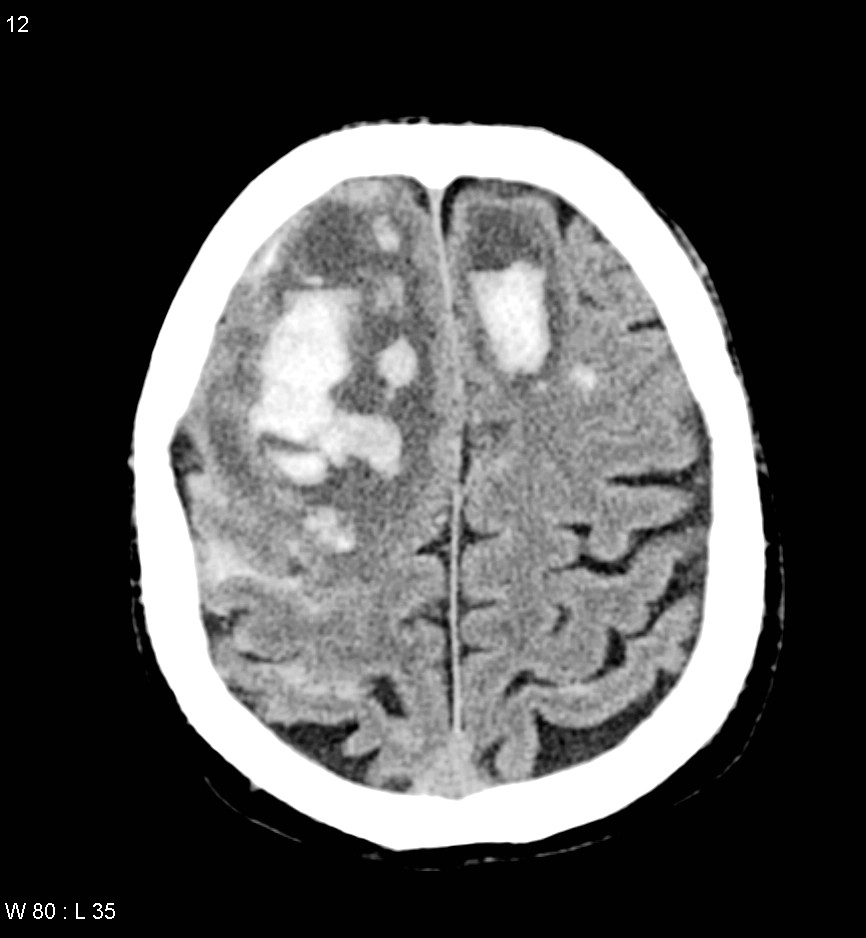
When interpreting the results, radiologists examine the images for any deviations from the normal anatomy. Abnormal findings on a CT scan mean that the scan does not fall within the normal range as per the radiologist's experience. These could include signs of bleeding, swelling, tumors, or other lesions. The scan can be acquired without intravenous contrast, but the addition of a radiopaque contrast agent administered intravenously helps to detect abnormal structural lesions such as brain tumors, brain abscesses, and vascular anomalies. With an intrathecal agent, the CT can outline abnormalities encroaching on the brain stem, spinal cord, or spinal nerve roots. These findings require further evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
In medical practice, CT scans of the head are covered when the documentation supports that the scan is reasonable and necessary, as stated by many healthcare regulations, and accurate coding information must be provided with claims to differentiate CT and/or MRI scans from other radiology services.
Brain CT scans offer detailed information about brain tissue and brain structures. Multiple axial sections are obtained through the brain from the skull base to the vertex. Brain and bone windows can be reconstructed in the coronal and sagittal plane.
The scans impact on healthcare extends beyond diagnosis, and the use of brain scans helps the medical team distinguish different kinds of abnormalities. The scans can sometimes provide a definitive diagnosis and at times it shows abnormal conditions inside the brain such as abnormal growth, lesions or tumours.
It's crucial to remember that an abnormal scan can indicate a benign abnormality, but it can also signify a life-threatening condition. From diagnosing acute injuries to detecting tumors, strokes, infections, and vascular disorders, CT imaging plays a critical role in the timely and accurate treatment of patients.
The following table offers a detailed breakdown of key aspects related to brain CT scans:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To visualize the brain and surrounding structures to identify abnormalities, diagnose conditions, and guide treatment. |
| Method | Uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain. The patient lies on a table that moves through a scanner. |
| Contrast Agent | A radiopaque contrast agent (often gadolinium) may be used to enhance the visibility of certain structures, particularly in cases of tumors, abscesses, or vascular issues. |
| What it Detects |
|
| Preparation |
|
| Risks |
|
| Benefits |
|
| Limitations |
|
| Billing Code | R94.02 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of abnormal brain scan. |
For further information, please consult with the following resourcesRadiologyInfo.org
CT scans of the head are essential in the rapid assessment of a variety of neurological conditions. They play an integral role in modern diagnostic imaging, offering insights into the complex structures and conditions affecting the brain and skull. These scans can assist in the early detection of serious conditions such as strokes, allowing for timely intervention and potentially improving patient outcomes. From diagnosing acute injuries to detecting tumors, strokes, infections, and vascular disorders, CT imaging plays a critical role in the timely and accurate treatment of patients.
In some cases, a CT scan of the head can identify conditions that might not be immediately apparent on other imaging techniques. For instance, in cases of head trauma, a CT scan can quickly identify skull fractures or bleeding in the brain, enabling prompt treatment and reducing the risk of long-term complications. Similarly, in the diagnosis of a stroke, a CT scan can differentiate between an ischemic stroke (caused by a blockage of blood flow) and a hemorrhagic stroke (caused by bleeding in the brain). The rapid determination of the type of stroke is crucial in guiding treatment decisions.
The scan provides a detailed report of all the normal and abnormal findings in the brain. This report is used by a medical team, including radiologists, neurologists, and other specialists, to help them distinguish between different kinds of abnormalities, many of which are benign and nothing to worry about.
It is useful to understand the importance of accurate interpretation. What are abnormal findings on a CT scan? Abnormal findings on a CT scan mean that your scan is not within the range of normal in the radiologists experience. An abnormal scan can mean that there is a benign abnormality, or it could mean there is a life-threatening condition that can lead to death without treatment.
The use of CT scans is not without its considerations. One of the primary concerns is the exposure to ionizing radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer over a lifetime. However, the benefits of early and accurate diagnosis often outweigh the risks. Modern CT scanners utilize techniques to minimize radiation exposure, making the procedure as safe as possible.
Another factor to consider is the possibility of allergic reactions to contrast agents, especially those containing iodine. Patients with a known allergy to iodine or other contrast agents should inform their healthcare provider before the scan. In some cases, alternative imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be more appropriate.
Beyond the specific diagnostic information they provide, CT scans of the head play a vital role in the overall management of patient care. For example, these scans can assist in the early diagnosis of brain tumors, which can be effectively treated with surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy if detected early. In cases of infections, such as brain abscesses, CT scans can help guide the drainage of the abscess and administer antibiotics. The timely diagnosis of vascular disorders such as aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) is also essential, allowing for the implementation of appropriate treatments to prevent bleeding and other complications.
In cases where a more detailed examination of brain tissues is necessary, physicians may order a brain MRI with contrast. This approach can give more detailed images. Some brain MRI exams use an injection of contrast material, and the contrast agent is often gadolinium, which is a rare earth metal.
The use of CT scans in healthcare extends beyond emergency situations. They are also employed in the diagnosis of chronic conditions. For example, CT scans can help detect signs of brain atrophy, which may be associated with conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. They can also be used to assess the severity of head injuries, and they can guide the selection of patients for further diagnostic tests or treatments. The application of CT scanning also extends to the evaluation of the head and neck.
It's important to remember that the interpretation of a CT scan is a complex process that requires the expertise of trained medical professionals. Radiologists, who specialize in interpreting medical images, are responsible for analyzing the scan results and providing a detailed report to the referring physician. The referring physician will then use this information to make a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan.
Diagnostic evaluation of the head and neck (head/neck scans) performed by computerized tomography (CT) scanners is covered when the documentation supports that the scan is reasonable and necessary. Accurate coding information must be provided with claims to differentiate CT and/or MRI scans from other radiology services and to make coverage.
The information provided in the CT scan report is crucial in informing the patient and their family about the diagnosis and the next steps in the treatment plan. The medical team works closely with the patient and their family to explain the findings of the scan in a clear and understandable manner and answer any questions they may have. This collaborative approach is essential in ensuring the patient receives the best possible care.
The future of brain CT scans is likely to involve further advancements in imaging technology, leading to even more detailed and accurate diagnoses. Improvements in image processing algorithms, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are expected to play a significant role in enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of CT scans. These advancements could lead to earlier detection of diseases, improved treatment planning, and better patient outcomes.
The evolution of CT technology has also influenced patient care in other ways. As a consequence, CT is less subject to motion artifact than in the past, although significant patient motion may still render images uninterpretable. The use of lower radiation doses, faster scan times, and improved image quality is making CT scans a safer and more valuable tool for patients.
Brain CT scans are indispensable tools in the field of medicine, providing invaluable information for the diagnosis and management of a wide range of conditions. From diagnosing acute injuries to detecting tumors, strokes, infections, and vascular disorders, CT imaging plays a critical role in the timely and accurate treatment of patients. Understanding the significance of CT scans can help patients make informed decisions about their health and advocate for the best possible care.
![CT Scan Brain Purpose, Results & Cost [2025] • Bookmerilab](https://bookmerilab.com/tests/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Normal-Vs-Abnormal-Ct-Scan-Brain.jpg)

Detail Author:
- Name : Audrey Walter PhD
- Username : ullrich.kayley
- Email : jess90@wintheiser.com
- Birthdate : 2000-12-13
- Address : 494 Dell Orchard Apt. 097 Pacochafurt, MO 10683-6001
- Phone : +1-724-218-9936
- Company : Brown-Lesch
- Job : Home Health Aide
- Bio : Quia quos veritatis quibusdam nam qui et et. Enim corporis ut rerum numquam vitae iure. Voluptas dolores quos voluptas dolorem aliquam eos et.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/mabelle_real
- username : mabelle_real
- bio : Quisquam nemo earum corporis suscipit temporibus. Vel cumque qui voluptatibus esse velit sint similique. Quibusdam voluptatem et et laudantium.
- followers : 4868
- following : 1259
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@mabelle_dev
- username : mabelle_dev
- bio : Quibusdam qui nemo natus velit deserunt temporibus.
- followers : 5659
- following : 2446
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/mkrajcik
- username : mkrajcik
- bio : Minima harum qui nulla veniam error.
- followers : 1076
- following : 2845
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/mabelle3879
- username : mabelle3879
- bio : Officia quidem corrupti assumenda aperiam voluptatem inventore.
- followers : 5226
- following : 2033